Ensuring your child’s dental health is just as important as monitoring their physical growth. Whether you’re looking for a trusted pediatric dentist in Palm Jumeirah, or simply trying to understand the best care for your little one, this guide is here to help. as monitoring their physical growth. Pediatric dental procedures are essential tools that keep your child’s smile healthy and bright. This comprehensive guide simplifies common pediatric dental procedures, preventive measures, and offers clear, detailed advice for maintaining your child’s oral health throughout their developmental years.
Why Pediatric Dental Procedures Matter
Many parents underestimate the importance of baby teeth, thinking they eventually fall out anyway. However, baby teeth play a crucial role in speech development, nutritional intake, and maintaining proper spacing for permanent teeth. Addressing dental issues early prevents serious future complications, including orthodontic problems, speech difficulties, and nutritional concerns.
Baby teeth guide the development and placement of permanent teeth. Early tooth loss or severe decay can lead to spacing issues and misalignment, making orthodontic treatments necessary later. Healthy baby teeth ensure proper chewing, essential for digestion and nutritional absorption. Furthermore, clear speech heavily depends on healthy teeth and correct jaw alignment, helping avoid speech impediments.
Preventive Dental Care: Starting Right
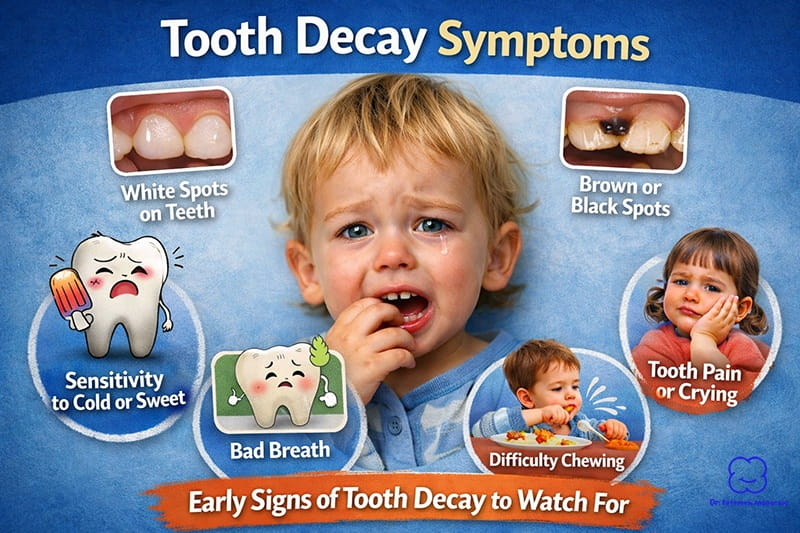
Prevention is undoubtedly the best strategy regarding pediatric dental procedures. Approximately 20% of children aged 5-11 years have at least one untreated decayed tooth, according to the CDC. Early preventive care dramatically reduces this percentage and ensures lifelong healthy habits.
Daily Oral Hygiene Habits
Establishing daily brushing and flossing routines is critical. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly from around age eight or nine can significantly reduce the risk of cavities. Making brushing enjoyable using flavored toothpaste or colorful toothbrushes can foster positive habits early. Parents modeling excellent oral hygiene behavior by brushing and flossing alongside their children reinforces the significance of regular dental care.
Read more: Best Toothbrush for Kids
Healthy Diet Choices
Limiting sugary snacks and beverages is crucial in protecting tooth enamel. Encouraging a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products can help neutralize harmful acids and strengthen teeth. Foods like cheese and yogurt boost enamel strength due to their calcium content. Additionally, crunchy fruits and vegetables like apples, celery, and carrots naturally clean teeth by stimulating saliva production, neutralizing acids, and washing away food debris.
If you’re struggling with this at home, check out our tips on how to stop kids eating too much sugar — practical advice tailored for families just like yours.
Regular Dental Checkups
Routine dental visits every six months are essential. These checkups allow pediatric dentists to closely monitor tooth development, identify early signs of potential issues, and provide preventive treatments such as fluoride applications. Regular dental visits also serve as educational opportunities for parents and children about oral hygiene practices, dietary guidance, and new dental care products.
Essential Preventative Pediatric Dental Procedures
Preventive procedures are the foundation of lifelong oral health for children, helping avoid discomfort and costly treatments later on.
Dental Cleanings
Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup, essential for preventing cavities and gum disease. During these visits, X-rays may be taken to monitor tooth and jaw development accurately. Fluoride treatments often follow cleanings, strengthening enamel and preventing decay. These quick, painless visits make them manageable and stress-free for children.
Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride treatments strengthen tooth enamel, significantly reducing the risk of cavities. Pediatric dentists commonly apply fluoride as gels, foams, or varnishes during regular checkups. These treatments are especially beneficial for children with higher cavity risks due to diet or genetic factors. Fluoride treatments can reduce decay risk by up to 30%, greatly minimizing the likelihood of more invasive dental procedures.
Dental Sealants
Dental sealants, thin protective coatings applied to molars and premolars, drastically reduce decay rates—by up to 80%. Sealants protect the chewing surfaces of teeth by blocking bacteria and food particles. They typically last around 10 years, making them an effective, long-term preventive measure. Sealants are particularly recommended during the critical age range of 6-14 years when permanent molars appear and are most susceptible to cavities.
Common Restorative Pediatric Dental Procedures
Despite robust preventive measures, some children will inevitably need restorative dental care.
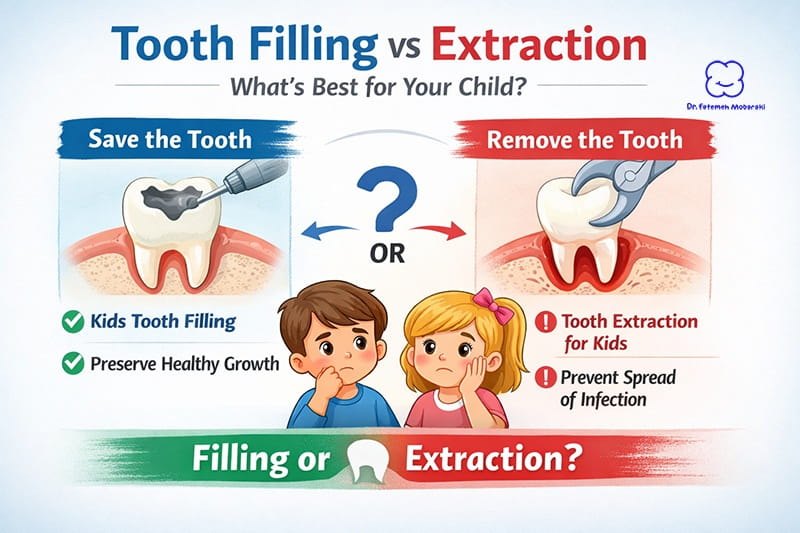
Cavity Treatments (Fillings)
Fillings address cavities—common issues due to children’s naturally weaker baby tooth enamel. Filling procedures involve removing decay and restoring the tooth with durable materials like composite resin, which blends naturally and is mercury-free. Addressing cavities promptly prevents worsening decay, potential tooth loss, and more invasive treatments such as root canals or crowns.
Dental Crowns
Dental crowns are necessary when teeth are significantly damaged or decayed beyond what fillings can restore effectively. Crowns reinforce tooth structure and functionality while blending aesthetically with surrounding teeth. Pediatric dental crowns often use stainless steel or ceramic materials, depending on the affected tooth’s location and parental preferences.
Tooth Extractions
Sometimes extractions become necessary due to extensive decay, severe infection, or significant overcrowding. Although extraction may initially seem intimidating, pediatric dentists perform this routine procedure safely and gently, often using sedation techniques to ensure comfort. Tooth extractions safeguard overall oral health by preventing infections or alignment issues.
Early Orthodontic Care
Early detection and treatment of orthodontic issues can significantly improve long-term outcomes. Problems like overcrowding, bite irregularities, or misaligned teeth in children, if untreated, can impact speech clarity, chewing efficiency, and overall oral health. Pediatric orthodontics, including braces and clear aligners, effectively address these issues during critical developmental periods, simplifying later treatments and potentially reducing costs.
Emergency Pediatric Dental Care
Children’s active lifestyles make them prone to dental injuries, such as chipped or knocked-out teeth. Pediatric dentists frequently manage such emergencies effectively, minimizing lasting damage. If you’re ever in need of emergency dental care for children in Dubai, it’s crucial to act quickly and see a pediatric dentist who can address the issue safely and gently. Parents should be prepared with emergency contacts and basic first-aid knowledge, such as keeping knocked-out teeth moist in milk or saliva until reaching professional care, ensuring swift and effective treatment.
Your Child’s First Dental Visit
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry advises scheduling your child’s first dental appointment around their first birthday. Early visits identify potential issues proactively and cultivate positive associations with dental care. Pediatric dental offices create welcoming, child-friendly environments to build trust, ease anxiety, and foster lifelong oral health habits.
By proactively engaging in regular dental visits, maintaining excellent oral hygiene, and understanding common pediatric dental procedures, parents can confidently ensure their children’s lasting oral health, creating a lifetime of beautiful, healthy smiles.
FAQs on Pediatric Dental Procedures
When should my child begin flossing?
Around ages eight or nine, when motor skills sufficiently develop for effective flossing.
How frequently should dental checkups occur?
Every six months is ideal for checkups and cleanings to maintain optimal oral health.
Are dental X-rays safe for children?
Yes, pediatric dental practices use digital, low-radiation X-rays, ensuring safety while closely monitoring development.