As a parent in Dubai, seeing your child in discomfort can be distressing, especially when it’s related to dental pain. One common issue pediatric dentists encounter regularly is a Dental Abscess in Kids. Understanding what a dental abscess is, recognizing its symptoms, and knowing when to seek professional help from a reliable kids dentist like Dr. Fatemeh Mobaraki can significantly reduce your child’s discomfort and prevent further complications.
Quick Facts:
- Dental abscesses cause severe pain and swelling.
- Immediate professional care is necessary.
- Prevention includes good oral hygiene and regular check-ups.
What Exactly is a Dental Abscess in Kids?
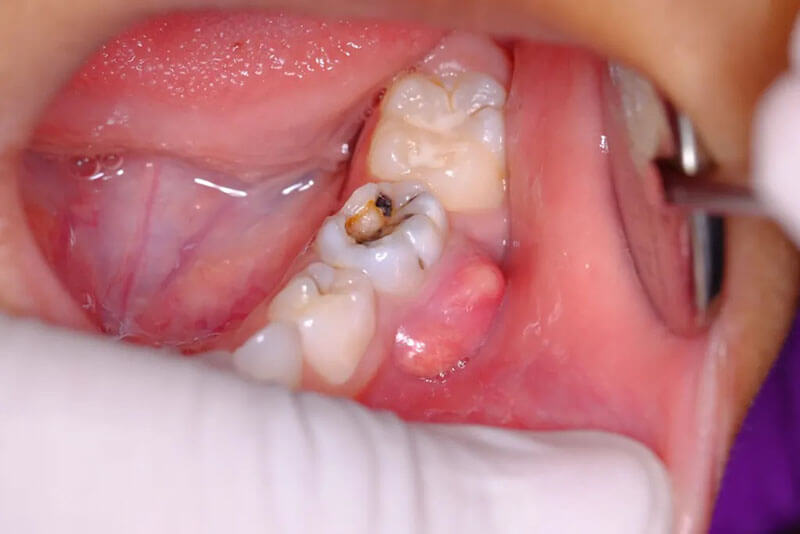
A dental abscess is a painful infection at the root of a tooth or between the gum and tooth, commonly resulting from untreated cavities in kids or dental trauma. Bacteria enter the tooth through cavities or cracks, leading to pus accumulation and severe inflammation.
Common Causes of Dental Abscess in Children
Several factors can lead to a dental abscess in children. Being aware of these common causes can empower parents to take proactive measures to protect their child’s dental health. Here’s an expanded look at the factors contributing to dental abscess in children:
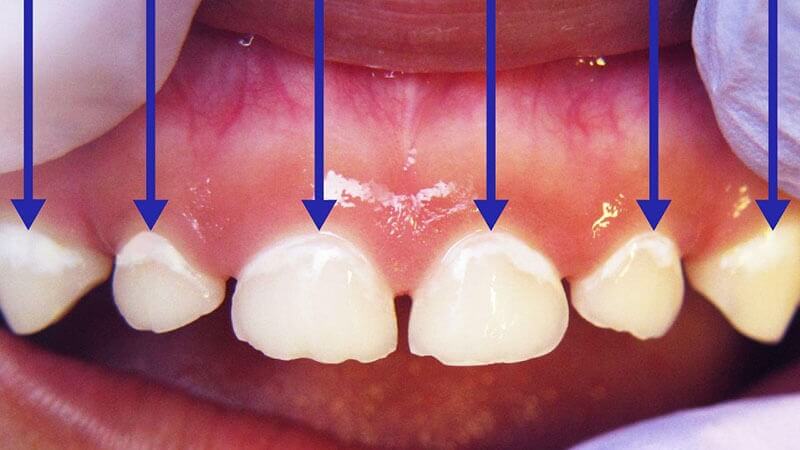
- Tooth decay: Untreated cavities are the primary cause of dental abscesses. Bacteria penetrate through cavities, infecting the tooth pulp and resulting in pus formation.
- Poor oral hygiene: Irregular or inadequate brushing and flossing lead to plaque accumulation, increasing the risk of cavities and subsequent abscess development.
- Dental trauma: Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can cause cracks or chips in teeth, providing bacteria easy access to the tooth pulp and creating ideal conditions for abscess formation.
- Infection after tooth filling: Occasionally, bacteria can become trapped beneath fillings if they are damaged or improperly placed, leading to infections and abscesses.
- Gum disease: While less common in children compared to adults, untreated gum inflammation (gingivitis in kids) can escalate into more serious infections, ultimately causing abscesses.
- Weak immune system: Children with compromised immune systems due to chronic illnesses, nutritional deficiencies, or other health conditions are more susceptible to infections, including dental abscesses.
- High sugar diet: Frequent consumption of sugary foods and beverages can rapidly accelerate tooth decay. Sugar provides nourishment to harmful oral bacteria, significantly increasing the likelihood of dental infections and abscess.
- Delayed dental visits: Skipping regular dental check-ups and delaying treatments allows minor dental issues to progress into severe infections, increasing abscess risk.
Understanding these causes allows parents to prioritize preventive dental care effectively, reducing the chance of their children experiencing painful dental abscesses.
Read more: What is Pediatric Pulp Therapy?
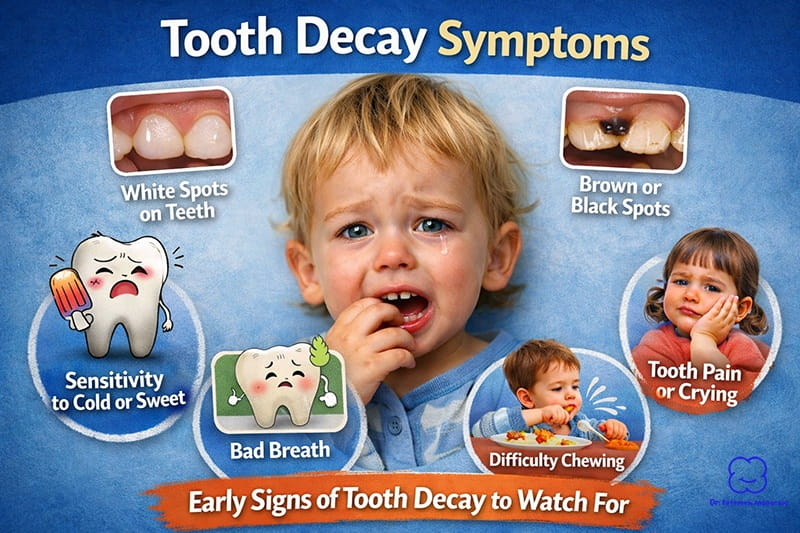
How to Recognize a Dental Abscess in Your Child?
Early identification of a dental abscess in children is critical for quick and effective treatment. Parents should be vigilant and observant, as children may not always communicate their discomfort clearly. Watch closely for these common signs:
- Persistent Toothache: A constant or recurring toothache that intensifies when biting or chewing is a strong indicator of an abscess.
- Sensitivity: Extreme sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks often accompanies a tooth infection.
- Redness and Swelling of Gums: The affected gum area may appear red, swollen, and tender to the touch, signaling infection and inflammation.
- Facial Swelling: Noticeable swelling of the cheeks, jaw, or face, particularly near the infected tooth, may occur as the abscess worsens.
- Fever and General Discomfort: A child with a dental abscess may experience a low-grade fever, indicating that the infection might be spreading beyond the tooth itself.
- Bad Breath and Unpleasant Taste: An unusual or persistent foul odor and taste in your child’s mouth could indicate an abscess.
- Difficulty Opening Mouth: Severe infections can lead to difficulty opening the mouth fully, causing discomfort while speaking or eating.
If your child shows any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate consultation with a pediatric dentist like Dr. Fatemeh Mobaraki to prevent complications and effectively manage the condition.
Dr. Fatemeh Mobaraki, a trusted pediatric dentist in Dubai, emphasizes,
“Early detection and intervention are key when dealing with dental abscess in children. Parents should never ignore symptoms, as prompt treatment can save teeth and protect overall health.”
What Are the Risks of Leaving a Dental Abscess Untreated?
Untreated dental abscesses can cause:
- Spread of infection to other areas like the jawbone or neck.
- Tooth loss and surrounding tooth damage.
- Sinusitis or chronic dental infections.
- Systemic infections impacting overall health.
Prompt emergency dental care for children prevents these outcomes.
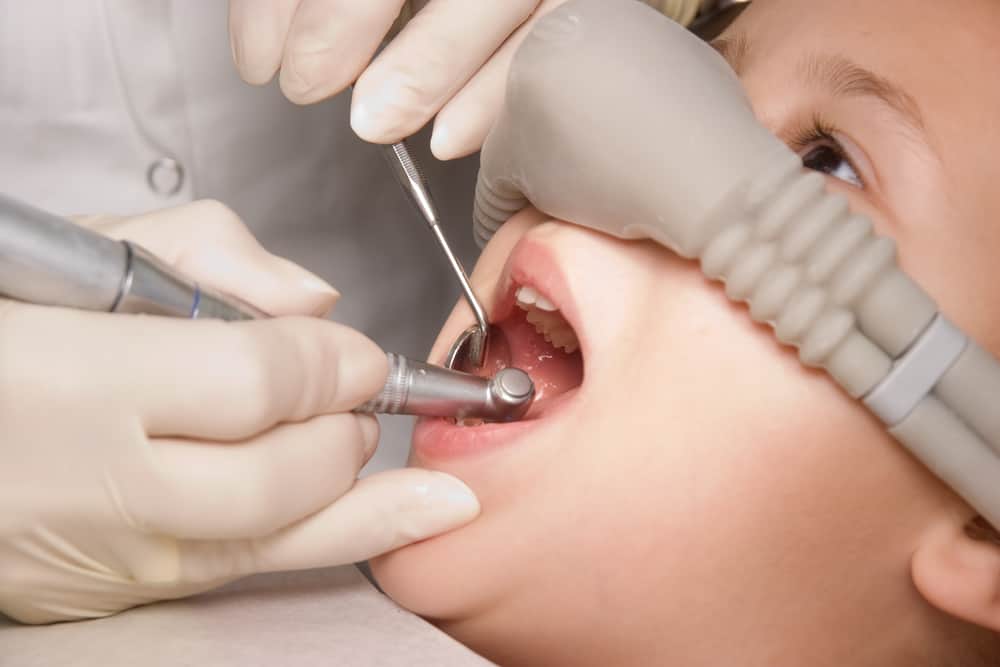
How is a Dental Abscess Diagnosed in Children?
At our pediatric dental clinic, Dr. Fatemeh Mobaraki ensures your child feels safe and relaxed. The evaluation includes:
- Medical and dental history review to identify influencing factors.
- Clinical examination for infection signs.
- Dental X-rays to assess the infection’s extent.
- Discussion of findings and personalized treatment planning.
Our approach ensures a positive experience for your child.
What Treatment Options are Available for Dental Abscess in Kids?
Dr. Mobaraki carefully selects treatments based on the abscess severity and your child’s individual dental needs. The goal of treatment is to eliminate infection, relieve pain, and restore dental health effectively. Here are detailed treatment methods:
- Drainage: This is often the initial and most immediate relief method. Dr. Mobaraki makes a gentle, small incision in the abscess to drain out the pus, quickly alleviating pain and reducing swelling. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia to ensure comfort.
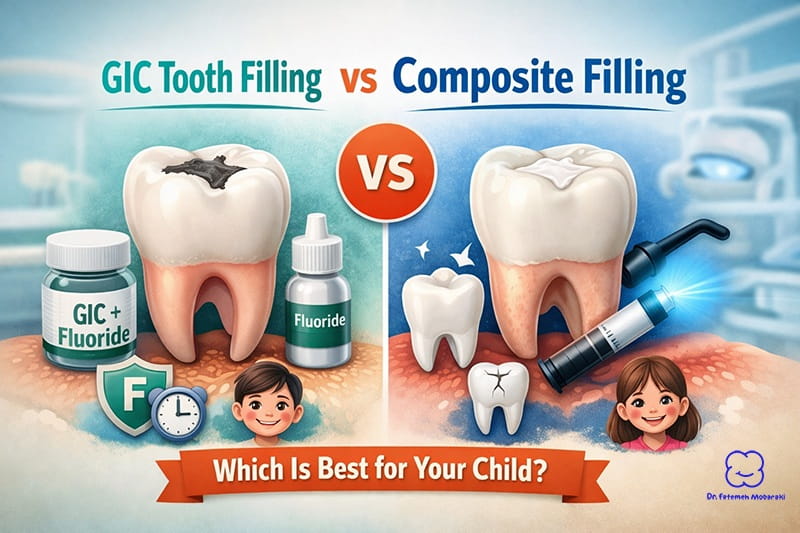
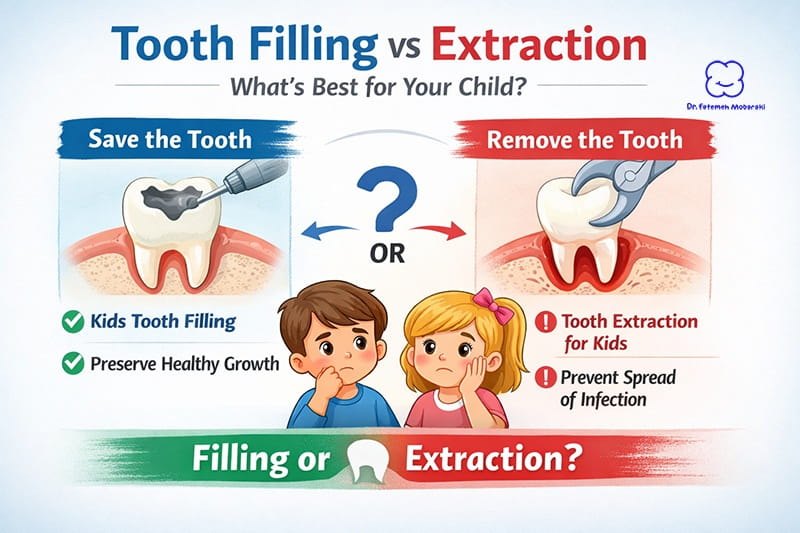
- Tooth filling for children: If the abscess is identified early and tooth damage is minimal, a tooth filling can effectively seal cavities and stop further bacterial entry, preventing abscess recurrence.
- Root canal therapy: In cases where the tooth infection is severe but the tooth structure can still be preserved, pediatric root canal treatment may be necessary. This involves removing infected pulp, thoroughly cleaning the tooth’s interior, and sealing it to prevent reinfection.
- Extraction: For severely damaged teeth or persistent infections, tooth extraction might be required. This is typically considered only when other treatments are unlikely to succeed. Following extraction, Dr. Mobaraki will discuss suitable options to preserve alignment and function, such as space maintainers.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are prescribed to manage infection effectively, especially if there is severe swelling, signs of systemic infection, or a high risk of infection spreading. It’s crucial to complete the entire antibiotic course to fully eliminate the infection.
- Dental crown for children: After abscess treatment, particularly root canal therapy, a dental crown may be placed to protect the weakened tooth structure, restoring its strength, appearance, and function. Pediatric dental crowns are highly durable and specifically designed to withstand daily wear and tear.
“According to the American Dental Association, untreated cavities can quickly lead to severe infections like dental abscesses.”
Home Care and Pain Relief Tips Before Visiting a Dentist
Manage your child’s discomfort temporarily by:
- Applying cold compresses.
- Administering child-safe pain relievers.
- Hydrating well and avoiding temperature extremes in food.
- Rinsing gently with warm saltwater.
Professional care is essential for lasting relief.
How Can Parents Prevent Dental Abscess in Children? Expert Advice
Preventing dental abscess in children is significantly more effective and less stressful than managing them once they occur. At our pediatric dental clinic, preventive care is emphasized as a fundamental aspect of maintaining your child’s oral health. Here are detailed expert recommendations to help you effectively minimize the risk of dental abscesses:
- Excellent oral hygiene: Teach your child to brush their teeth thoroughly at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, especially after meals. Encourage proper brushing techniques, focusing on all tooth surfaces and hard-to-reach areas. Daily flossing is also crucial for removing food particles and plaque buildup between teeth, which toothbrushes often miss.
- Regular dental check-ups: Scheduling routine visits to the dentist every six months enables early detection and prompt treatment of potential dental problems. Regular check-ups with Dr. Mobaraki help catch cavities or early signs of tooth decay before they lead to serious infections.
- Healthy diet: Limit the intake of sugary snacks and beverages, as excessive sugar consumption directly contributes to tooth decay. Replace sugary foods with healthier alternatives such as fruits, vegetables, cheese, and nuts that are beneficial for oral health.
- Dental sealants: Applying dental sealants, a protective plastic coating, on your child’s molars and premolars can significantly reduce the risk of cavities. Sealants provide a durable barrier against bacteria and food particles, preventing decay and subsequent abscess formation.
- Fluoride treatments: Professional fluoride treatments help strengthen tooth enamel, making teeth more resistant to decay and infection. Dr. Mobaraki can advise on fluoride varnishes or gels appropriate for your child’s age and dental condition.
- Proper hydration: Encourage your child to drink ample amounts of water, particularly fluoridated tap water, throughout the day. Good hydration maintains saliva production, which naturally cleanses the mouth and neutralizes acids, protecting against tooth decay.
- Sports protection: For active children involved in sports or physical activities, using a custom-fitted mouthguard helps prevent injuries that can lead to dental trauma, potentially causing abscesses and other dental issues.
By following these expert preventive measures consistently, you can help ensure your child maintains excellent oral health and significantly reduce their risk of developing a dental abscess.
How Common Are Dental Abscesses Among Kids in Dubai?
Dental abscess in children are relatively common in Dubai due to dietary habits and inconsistent oral hygiene. Increased awareness and preventive care significantly reduce risks.
What If Your Child’s Symptoms Begin to Improve on Their Own?
Symptom relief doesn’t mean the abscess is healed. Professional dental evaluation is necessary to avoid recurrence and complications.
When Should You See a Pediatric Dentist, and How Can We Help?
Visit our clinic immediately if your child shows persistent pain or swelling. Dr. Mobaraki specializes in emergency dental care for children, offering compassionate, comprehensive solutions.
Conclusion & Next Steps for Your Child’s Dental Health
Early detection and prompt treatment protect your child’s health and comfort. Our pediatric dental clinic is dedicated to superior, personalized dental care.
FAQs About Dental Abscess in Children
1. Is a dental abscess contagious?
No, a dental abscess itself is not contagious, but the bacteria causing it can potentially spread through saliva. Avoid sharing utensils, cups, or toothbrushes during an infection.
2. Can my child go to school with an abscessed tooth?
If your child has mild symptoms, they may be able to attend school, but it’s generally advisable to keep them home if they have significant pain, swelling, fever, or discomfort. Immediate dental care is essential in these cases.
3. How quickly should we see the dentist if my child has a dental abscess?
Ideally, you should see the dentist within 24 hours. Prompt evaluation helps prevent complications and ensures quicker recovery.
4. Will the dental abscess go away without treatment?
Symptoms might temporarily subside, but an abscess typically won’t heal on its own. Professional dental treatment is necessary to prevent recurrence or more severe health issues.