As parents, ensuring our children have healthy teeth and gums is a top priority. From brushing habits to diet, every detail matters. Visiting a trusted kids dentist in Dubai can help ensure your child’s teeth stay healthy while addressing common concerns like diet and oral hygiene.
One common question among parents in Dubai is, Is milk good for children’s teeth? Milk is often praised as a nutritional powerhouse for growing children, but how exactly does it impact their dental health? In this article, we’ll explore the role of milk in strengthening children’s teeth, its benefits, and alternatives for those who cannot or choose not to consume cow’s milk. We’ll also highlight how professional dental care, such as regular dental check-ups and oral hygiene services, can complement a healthy diet for optimal dental health.
The Role of Milk in Strengthening Children’s Teeth
Milk is a rich source of essential nutrients, particularly calcium and phosphorus, which are vital for the development of strong teeth and bones. Calcium helps in forming the hard outer layer of teeth, known as enamel, making them more resistant to decay. Phosphorus works alongside calcium to strengthen teeth and repair enamel.
Vitamin D, another critical nutrient found in milk, aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, ensuring these minerals reach the teeth and bones effectively. The combination of these nutrients in milk makes it a valuable addition to a child’s diet for dental health.
This makes milk an essential component of a diet designed to promote healthy teeth for kids.
Benefits of Milk for Children’s Teeth: Is Milk Good for children’s Teeth?
Here’s a summary of the key benefits of milk for dental health:
- Strengthens Enamel: Calcium and phosphorus reinforce the enamel, protecting against cavities.
- Reduces Acid Damage: Milk’s pH neutralizes acids, preventing enamel erosion.
- Provides Essential Nutrients: Vitamin D in milk enhances calcium absorption, supporting strong teeth and bones.
How Milk Prevents Tooth Decay
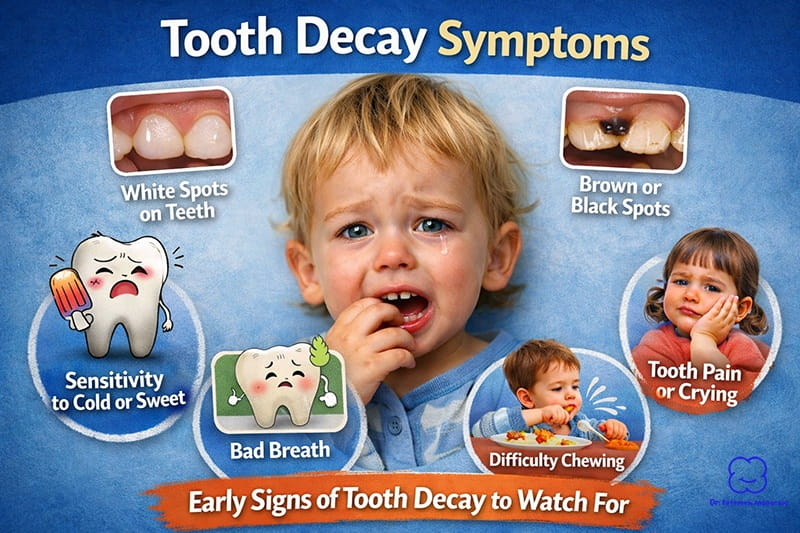
Tooth decay occurs when acids in the mouth erode the enamel. These acids are often produced by bacteria that feed on sugars left on teeth after eating. Milk helps in several ways:
- Neutralizing Acids: The high pH of milk can help neutralize harmful acids in the mouth, reducing the risk of enamel erosion.
- Stimulating Saliva Production: Drinking milk stimulates saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and bacteria from the teeth.
- Forming a Protective Barrier: The proteins in milk, such as casein, form a protective layer on the enamel, shielding it from acid attacks.
By incorporating milk into a child’s diet, parents can help reduce the risk of cavities and support long-term oral health.
Healthy Milk Consumption Habits for Dental Health
While milk offers significant benefits for dental health, how and when it’s consumed is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Avoid Bedtime Bottles: Milk should not be given right before bedtime without brushing, as it can leave sugars on the teeth overnight.
- Pair with Meals: Drinking milk during meals helps stimulate saliva production and washes away food particles.
- Limit Flavored Milk: Opt for plain milk instead of chocolate or strawberry versions, which often contain added sugars that can harm teeth.
By encouraging healthy milk consumption habits, parents can maximize its dental benefits.
Read more: Pacifier Teeth in Children
Lactose Intolerance and Dental Health
For children who are lactose intolerant, lactose-free milk is an excellent option. It contains the same beneficial nutrients as regular milk without causing digestive issues. Parents can also explore plant-based milk alternatives fortified with calcium and vitamin D. Consulting with a pediatrician or dentist can help determine the best choice for your child’s needs.
Cultural Preferences in Milk Consumption in Dubai
In Dubai, many families prefer alternatives like camel milk or goat milk, which are traditional to the region. Camel milk, for instance, is rich in nutrients and has a slightly higher calcium content than cow’s milk, making it a valuable option for children’s dental health. Goat milk is also a good source of calcium and may be easier to digest for some children.
Parents should ensure these options are part of a balanced diet to support strong teeth and overall health.
Alternatives to Milk for Strong Teeth
Not all children can consume cow’s milk due to lactose intolerance, allergies, or dietary preferences. Fortunately, there are several alternatives:
- Fortified Plant Milks: Almond, soy, oat, and coconut milk are often fortified with calcium and vitamin D, making them suitable substitutes.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and broccoli are excellent sources of calcium.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sesame seeds, and chia seeds provide calcium and other nutrients essential for dental health.
- Dairy Products: Yogurt and cheese are good alternatives for children who can tolerate dairy but prefer variety.
Parents should ensure these alternatives are free of added sugars, as excessive sugar can lead to cavities.
How Much Milk Can Kids Drink?
| Age Group | Recommended Milk Intake |
|---|---|
| Toddlers (1-2 years) | 2-3 cups (16-24 ounces) |
| Children (2-8 years) | 2 cups (16 ounces) |
| Older Children (9+ years) | 3 cups (24 ounces) |
Leading organizations like the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry emphasize that plain cow’s milk and water are the healthiest drink options for children between the ages of one and five to support their growth and dental health.
Excessive milk consumption can interfere with iron absorption, so it’s important to balance milk intake with other nutrient-rich foods.
Should Kids Drink Plant Milks Instead of Cow’s Milk?
Plant-based milks are increasingly popular, but are they as effective as cow’s milk for dental health? Fortified plant milks can provide similar levels of calcium and vitamin D, but they often lack the natural casein protein found in cow’s milk, which helps protect enamel.
Parents opting for plant-based milks should choose fortified versions and ensure their children consume other calcium-rich foods to maintain dental health.
How We Can Help You
At Dr. Fatemeh Mobaraki’s pediatric dental clinic in Dubai, we’re committed to helping parents nurture their children’s dental health. Our services include:
- Oral Hygiene Education: Teaching children and parents the importance of proper brushing and flossing techniques.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Detecting and addressing dental issues early on.
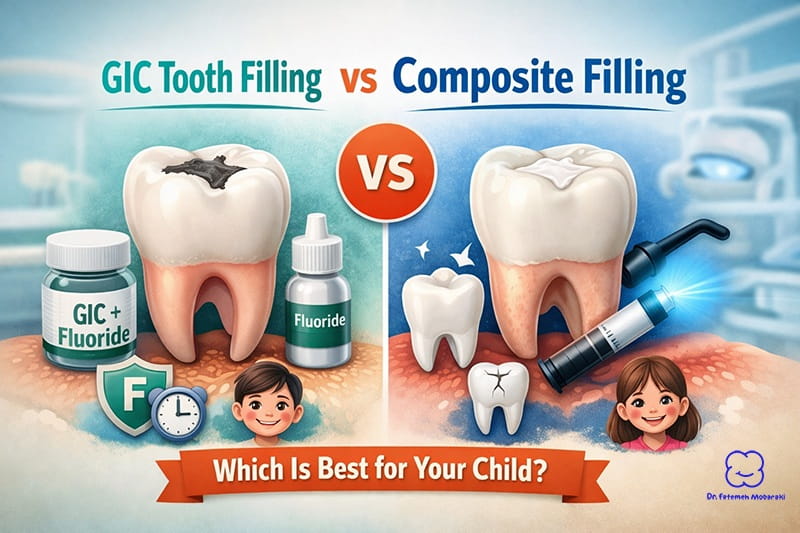
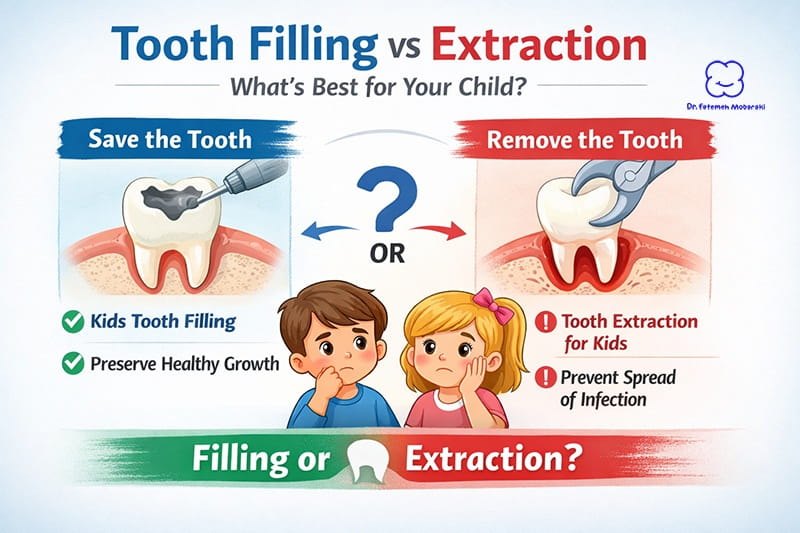
- Tooth Fillings for Children: Providing effective treatments for cavities caused by dietary habits or other factors.
If you’re concerned about your child’s dental health, our team is here to guide you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Milk is undoubtedly beneficial for children’s teeth, thanks to its calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D content. However, maintaining proper dental hygiene and monitoring how milk is consumed are equally important. For parents in Dubai seeking expert advice and care, Dr. Fatemeh Mobaraki’s clinic offers comprehensive services to ensure your child’s smile remains healthy and bright. Schedule a visit today to learn more about how we can support your family’s dental needs.
In summary, the answer to the question, Is milk good for children’s teeth?, is a resounding yes, as long as it’s consumed in moderation and accompanied by good dental care.
FAQs
1. Can milk cause cavities in children?
Milk itself doesn’t cause cavities, but prolonged exposure to its natural sugars, especially during bedtime, can lead to tooth decay. Proper brushing habits can prevent this.
2. What type of milk is best for children’s teeth?
Cow’s milk is ideal due to its natural calcium, phosphorus, and casein protein. Fortified plant milks are suitable alternatives for those who cannot consume cow’s milk.
3. How can I prevent baby bottle tooth decay?
Avoid letting your child fall asleep with a bottle of milk. Ensure their teeth are cleaned before bedtime.
4. When should my child have their first dental check-up?
It’s recommended to visit a dentist by their first birthday or within six months of their first tooth erupting.