As a pediatric dentist in Dubai, one of the primary concerns parents often raise is the distinction between dental plaque and tartar. Both are common issues that can affect oral health, especially in children. Understanding the key differences between Dental Plaque vs Tartar and knowing how to prevent these conditions is essential for maintaining your child’s healthy smile.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into what dental plaque and tartar are, the risks they pose, and the steps parents can take to ensure their child’s teeth and gums remain healthy and strong.
What is Dental Plaque?
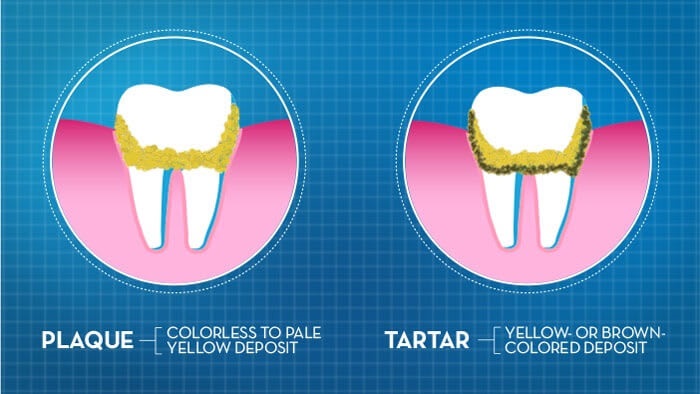
Dental plaque is a soft, sticky, and colorless film that continuously forms on the surface of your child’s teeth and along the gumline. It’s a natural byproduct of bacteria present in the mouth mixing with food particles and saliva. While plaque itself is normal, allowing it to build up can lead to serious oral health issues.
Formation:
Plaque starts to form shortly after eating. When sugars and starches from food combine with bacteria, they produce acids that can attack tooth enamel, increasing the risk of cavities.
Why is Plaque Harmful?
If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar (also called calculus), which is much more difficult to remove. Plaque buildup can lead to a range of oral health issues, including:
- Cavities: The acids produced by plaque bacteria weaken the tooth enamel, creating holes or cavities in the teeth.
- Gingivitis: If plaque is not removed, it can irritate the gums, causing inflammation and the early stages of gum disease.
Prevention:
The best way to prevent plaque from turning into a serious problem is through proper oral hygiene:
- Brushing: Your child should brush their teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, ensuring all surfaces are cleaned.
- Flossing: Daily flossing helps remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth and under the gumline.
- Diet: A balanced diet with limited sugary and starchy foods can also help reduce plaque buildup.
What is Tartar?
While plaque is relatively easy to remove with routine oral care, tartar is a more stubborn issue. Tartar forms when plaque is left on the teeth for too long and hardens due to the minerals in saliva. Tartar is much harder than plaque and cannot be removed by brushing or flossing alone. It typically forms above and below the gumline, leading to more severe oral health problems.
Formation:
Tartar begins to develop within 24 to 72 hours if plaque isn’t removed. Once it hardens, it provides an even better surface for more plaque to accumulate, further compounding the problem.
Why is Tartar Harmful?
Tartar poses several serious risks to your child’s oral health:
- Periodontal Disease: Tartar buildup can irritate and inflame the gums, eventually leading to gum disease. If left untreated, this can progress into periodontal disease, where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that can become infected.
- Discoloration: Tartar is often yellow or brown and can stain your child’s teeth. This can affect their confidence in their smile.
- Further Plaque Accumulation: Tartar is rough and porous, providing an ideal surface for plaque to attach, leading to a continuous cycle of plaque and tartar buildup.
Treatment:
Since tartar is hard and firmly attached to the teeth, it cannot be removed by brushing or flossing at home. It requires professional dental care:
- Dental Cleaning: Your pediatric dentist will use special instruments to remove tartar from the teeth, both above and below the gumline. This process is called scaling.
- Routine Checkups: Regular visits to the dentist are key to preventing tartar buildup. During these checkups, your child’s teeth will be professionally cleaned to remove any plaque or tartar that has accumulated.
Dental Plaque vs Tartar: Key Differences
While both plaque and tartar are harmful, there are distinct differences between them:
- Texture and Appearance: Plaque is soft, sticky, and often colorless or pale yellow, whereas tartar is hard, rough, and usually yellow or brown.
- Removal: Plaque can be easily removed with regular brushing and flossing, while tartar requires professional cleaning.
- Health Impact: Both plaque and tartar contribute to cavities and gum disease, but tartar poses a greater risk for more advanced gum disease due to its hardened nature.
Plaque and Tartar in Children: Prevention and Treatment
Children are particularly vulnerable to both plaque and tartar buildup due to their developing oral hygiene habits. Ensuring that your child adopts good oral care practices is key to preventing these issues.
Prevention Tips for Parents:
- Daily Brushing and Flossing: Encourage your child to brush their teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque before it hardens into tartar.
- Healthy Diet: Limit sugary snacks and drinks, as sugars feed the bacteria that form plaque.
- Use of Fluoride: Fluoride helps to strengthen tooth enamel and make it more resistant to decay caused by plaque acids. Make sure your child uses fluoride toothpaste and consider asking your dentist about fluoride treatments.
- Regular Dental Visits: Bring your child to the dentist every six months for routine cleanings and checkups. Early detection and removal of plaque and tartar can prevent more serious dental issues from developing.
Why Choose a Pediatric Dentist in Dubai?
Choosing a pediatric dentist in Dubai means your child will receive specialized care tailored to their needs. Pediatric dentists are trained to work with children, ensuring that their dental visits are comfortable and stress-free. Regular checkups with a pediatric dentist will not only help maintain your child’s oral health but also establish positive dental habits that will last a lifetime.