Parents often notice small changes first—a child avoiding cold drinks, chewing on one side, or complaining of “something stuck” in a tooth. These early signs can point to underlying dental issues. Understanding the types of dental diseases that affect children helps parents act early and prevent more serious problems.
As a kids dentist in dubai, I often see how quickly small dental concerns in children can develop into more complex conditions when early signs are missed. Children’s teeth, especially primary teeth, are more vulnerable than adult teeth. Their enamel is thinner, their habits are still developing, and their diet often includes cavity-friendly foods. Because of this, recognizing different children dental problems is not just helpful—it’s essential.
What are the most common types of dental diseases in children?
The most common types of dental diseases in children include tooth decay (cavities), gum disease, enamel defects, dental infections, and early tooth loss. These conditions vary in severity, but all benefit from early attention.
1. Tooth Decay (Dental Caries)

This is the most widespread condition among pediatric dental diseases. It occurs when bacteria break down sugars and produce acids that weaken enamel.
Early signs:
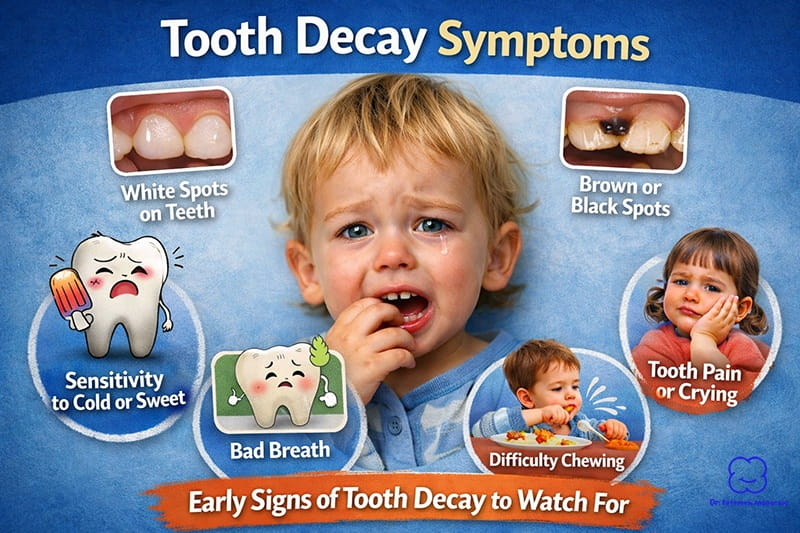
- White spots on teeth
- Sensitivity to sweets or cold
- Visible holes or dark areas
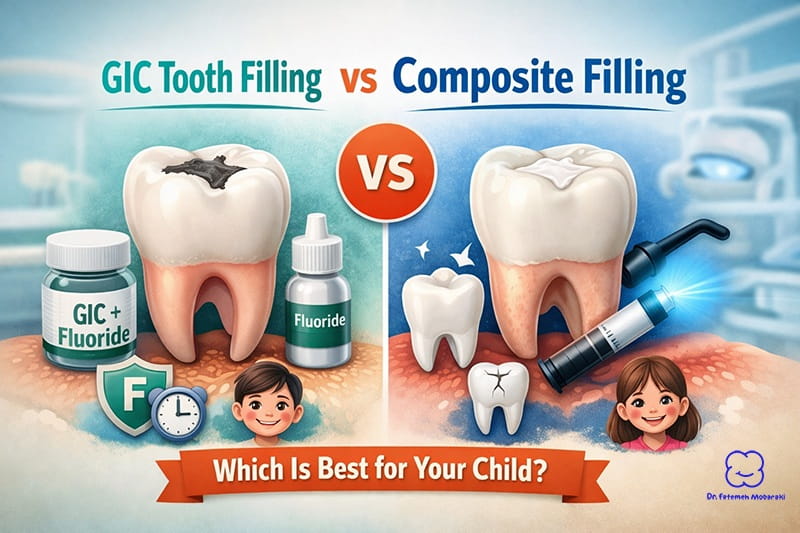
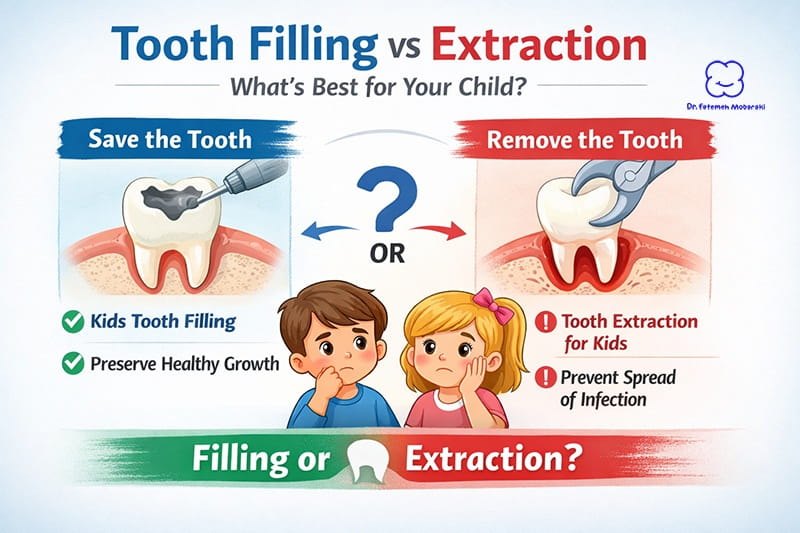
If untreated, decay may require treatments such as tooth filling in kids to restore the tooth and prevent further damage.
2. Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
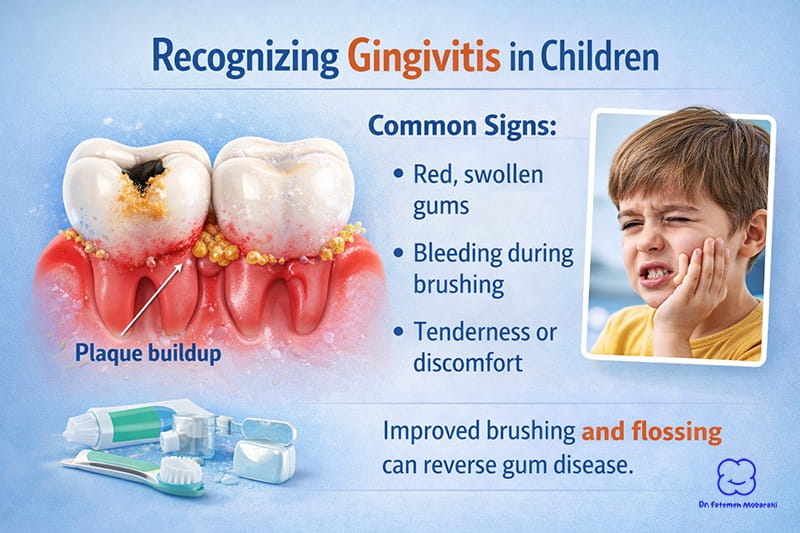
Gum inflammation is less discussed but still part of common dental diseases in children. It is usually caused by plaque buildup along the gumline.
Signs include:
- Red or swollen gums
- Bleeding during brushing
- Mild discomfort
The good news is that gingivitis in kids is reversible with proper oral hygiene.
3. Enamel Defects (Enamel Hypoplasia)
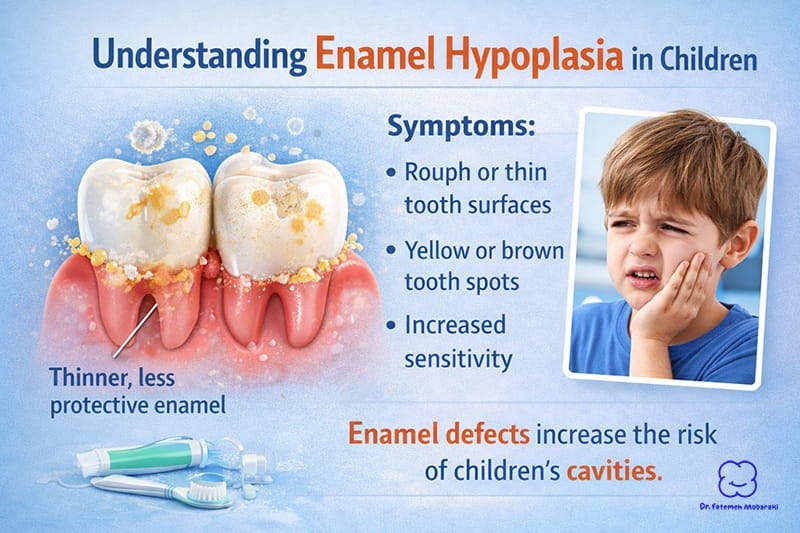
This condition affects how the enamel forms, making teeth thinner and more vulnerable.
Children may have:
- Yellow or brown patches
- Rough or uneven tooth surfaces
- Increased sensitivity
These teeth are more prone to decay and may require closer monitoring.
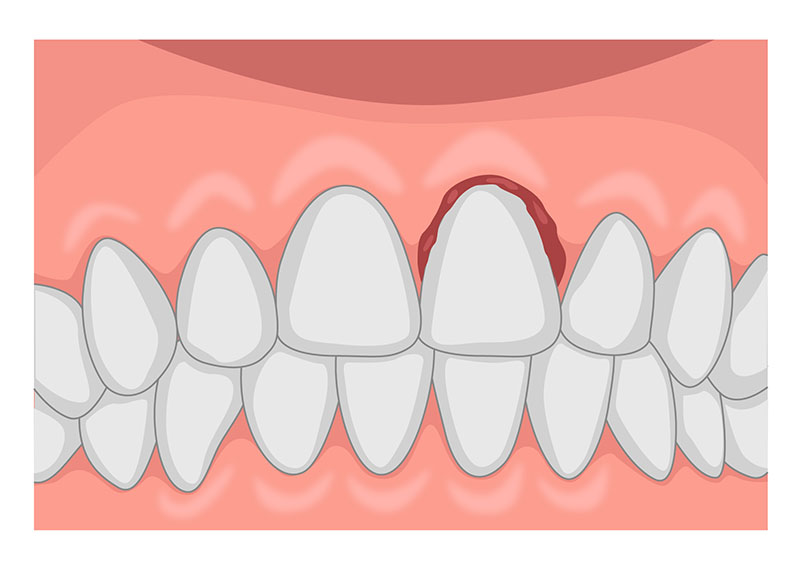
4. Dental Infections (Pulpitis and Abscess)
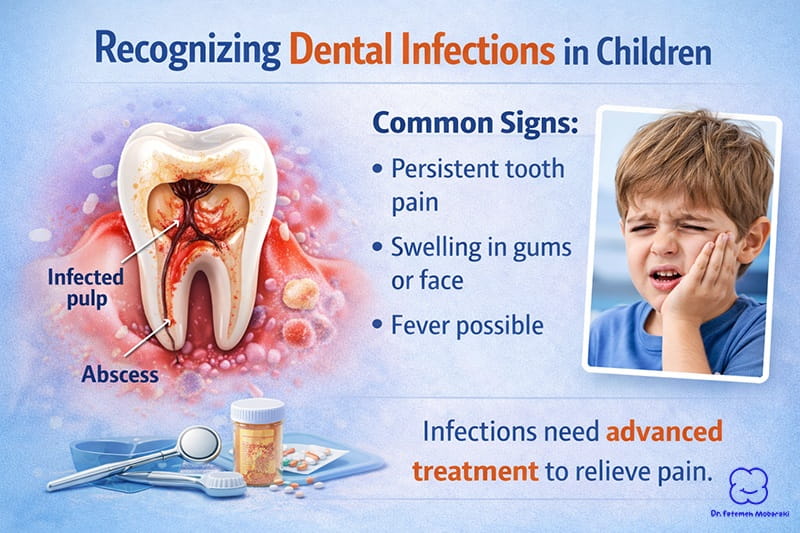
When decay is left untreated, bacteria can reach the inner tooth structure and cause infection.
Common signs:
- Persistent tooth pain
- Swelling in gums or face
- Fever in more severe cases
These conditions may require more advanced treatment to control infection and relieve pain.
5. Early Tooth Loss
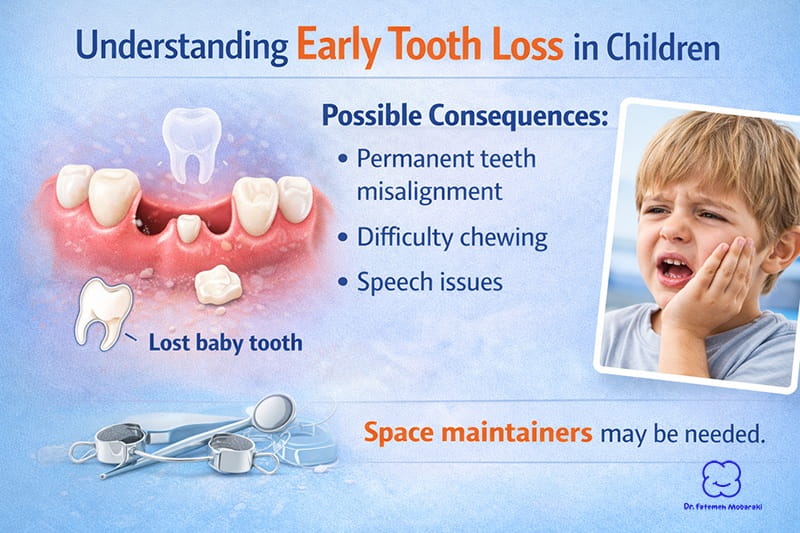
Losing baby teeth too early—often due to decay or trauma—can affect how permanent teeth grow.
Possible consequences:
- Misalignment of adult teeth
- Difficulty chewing
- Speech development concerns
In some cases, space management may be needed to guide proper dental development.
Why do children develop dental diseases more easily?
Children develop dental diseases more easily due to a combination of biological and behavioral factors. Their enamel is softer, and their brushing habits are still developing.
Several contributing factors include:
- Frequent snacking or sugary drinks
- Nighttime feeding without cleaning teeth
- Inconsistent brushing routines
- Limited fluoride exposure
- Deep grooves in molars that trap food
Even healthy diets can contribute if oral hygiene is not consistent. For example, natural sugars in juices can still feed bacteria.
Parents often underestimate how quickly these issues progress. What starts as a small enamel change can turn into a cavity within months.
How can parents recognize early signs of dental problems?
Early detection is one of the most effective ways to manage types of teeth diseases in children. Most dental conditions start quietly and worsen over time.
Watch for these signs at home:
- Complaints of tooth pain or sensitivity
- Avoiding certain foods (especially cold or sweet)
- Visible discoloration (white, brown, or black spots)
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away
- Swelling around gums or face
In some cases, children may not complain at all. Behavioral changes—like irritability during meals—can be an indirect signal.
If damage progresses, more protective treatments such as a dental crown for child may be recommended to preserve the tooth structure.
What types of dental infections can occur in children?
Dental infections are more serious forms of pediatric dental diseases and require prompt care. They usually develop when untreated decay reaches the inner layers of the tooth.
Pulp Infection (Pulpitis)
This occurs when bacteria reach the pulp (nerve tissue). It can cause:
- Persistent pain
- Sensitivity to temperature
- Discomfort when chewing
Dental Abscess
An abscess is a pocket of infection that can form at the root of a tooth.
Signs include:
- Swelling in the gums or face
- Fever
- Severe pain
- Pus discharge
These infections can affect a child’s overall health if left untreated. In some cases, especially when a child is very young or anxious, treatment may involve general anesthesia for kids dental work to ensure safety and comfort.
How does baby bottle tooth decay fit into these conditions?
Baby bottle tooth decay is a specific and preventable form of tooth decay that falls under common dental diseases in children. It happens when teeth are frequently exposed to sugary liquids, especially during sleep.
This includes:
- Milk
- Formula
- Juice
The risk increases when a child falls asleep with a bottle, allowing sugars to stay on teeth for extended periods.
Parents looking to understand this better can read Baby Bottle Tooth Decay post as a detailed topic, as it often progresses faster than typical cavities.
Are all dental problems in children visible?
No, not all types of dental diseases are immediately visible. Some develop beneath the surface or between teeth where they are harder to detect.
For example:
- Early cavities may not be seen without proper lighting
- Gum inflammation may be subtle
- Bite issues or alignment problems may only appear over time
Regular dental checkups help identify these hidden issues. Preventive care is often less invasive and more comfortable for children than treating advanced conditions.
Parents often gain a better understanding of what to expect during visits by reviewing common Pediatric dental procedures, which explains routine and preventive treatments.
What role does diet play in children dental problems?
Diet plays a direct and continuous role in the development of children dental problems. Every time a child eats, especially sugary or starchy foods, bacteria in the mouth produce acids.
Key dietary risk factors include:
- Sticky snacks (candies, dried fruit)
- Frequent juice consumption
- Processed carbohydrates (chips, crackers)
- Sugary cereals
However, it’s not just what children eat—it’s how often they eat. Frequent snacking doesn’t allow saliva enough time to neutralize acids.
Balancing meals and encouraging water between snacks can significantly reduce risk.
How is pediatric dental care approached in Dubai?
In Dubai, pediatric dental care is structured around prevention, early diagnosis, and child-friendly treatment approaches. Clinics focus on making children comfortable while addressing both simple and complex dental conditions.
Parents searching for a reliable kids dentist in dubai often look for professionals trained in behavior guidance, preventive care, and minimally invasive treatments.
The environment also plays a role. Clinics designed for children help reduce anxiety, making it easier to manage conditions before they worsen.
Dr. Fatemeh Mobaraki, for example, emphasizes early monitoring and preventive strategies tailored to each child’s developmental stage.
How do different types of dental diseases affect long-term oral health?
Untreated types of teeth diseases can impact more than just a child’s current comfort. They may influence speech development, nutrition, and even the alignment of permanent teeth.
Possible long-term effects include:
- Premature tooth loss leading to spacing issues
- Difficulty chewing, affecting nutrition
- Increased risk of infections
- Anxiety related to dental visits
Understanding restorative options—such as those discussed in Types of Dental Crowns for Kids—can help parents feel more prepared if intervention becomes necessary.
The earlier a condition is addressed, the simpler and more effective the treatment tends to be.
Expert insight: Why early prevention matters
From a clinical perspective, most pediatric dental diseases are preventable with consistent oral hygiene, fluoride exposure, and regular dental visits. Research consistently shows that early intervention reduces the need for invasive procedures and improves long-term oral health outcomes.
Conclusion
Children can experience a wide range of dental conditions, from mild gum irritation to more serious infections. Recognizing the types of dental diseases early allows parents to respond calmly and effectively.
Small signs—like sensitivity, discoloration, or changes in eating habits—are often the first indicators. With proper care, most issues can be managed before they become complex.
A steady routine of brushing, balanced nutrition, and regular dental checkups provides a strong foundation. Over time, these habits not only protect teeth but also help children feel confident and comfortable with their oral health.